Traditional painting involves essentially the same techniques as calligraphy and is done with a brush dipped in black or colored ink; oils are not used. As with calligraphy, the most popular materials on which paintings are made of are paper and silk. The finished work can be mounted on scrolls, such as hanging scrolls or handscrolls. Traditional painting can also be done on album sheets, walls, lacquerware, folding screens, and other media.
The two main techniques in Chinese painting are:
- Gong-bi (??), meaning “meticulous”, uses highly detailed brushstrokes that delimits details very precisely. It is often highly coloured and usually depicts figural or narrative subjects. It is mostly practised by artists working for the court or in independent workshops.
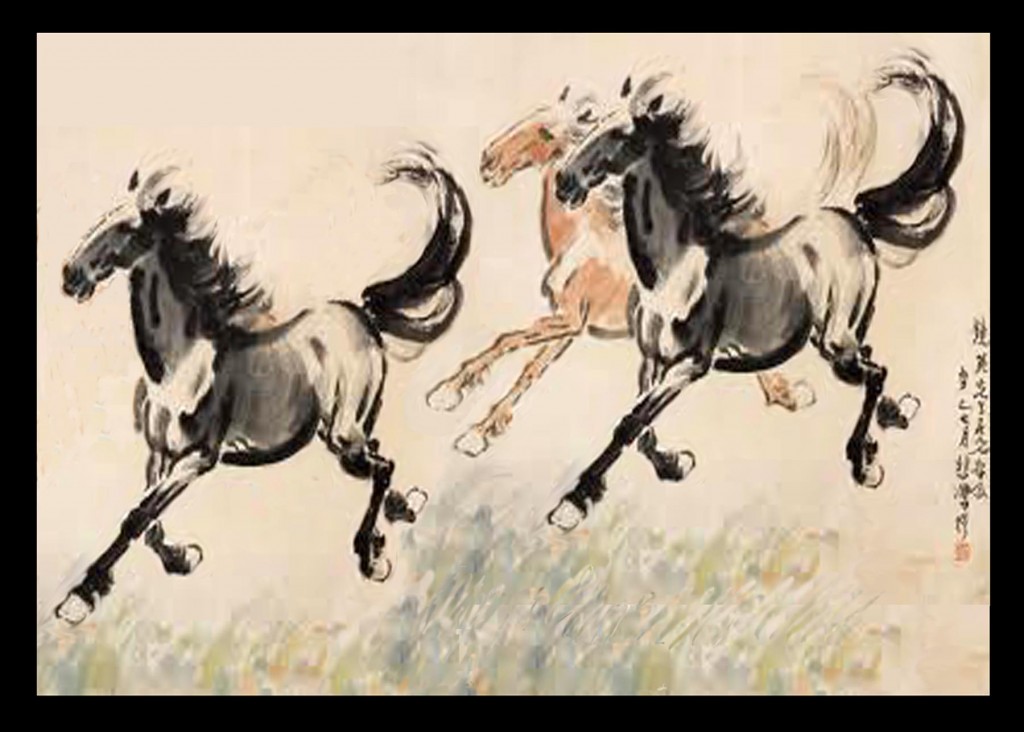
- Ink and wash painting, in Chinese Shui-mo or (??[1]) also loosely termed watercolour or brush painting, and also known as “literati painting”, as it was one of the “Four Arts” of the Chinese Scholar-official class.[2] In theory this was an amateur art practised by gentlemen, a distinction that begins to be made in writings on art from the Song dynasty, though in fact the careers of leading exponents could benefit considerably.[3] This style is also referred to as “xie yi” (??) or freehand style.
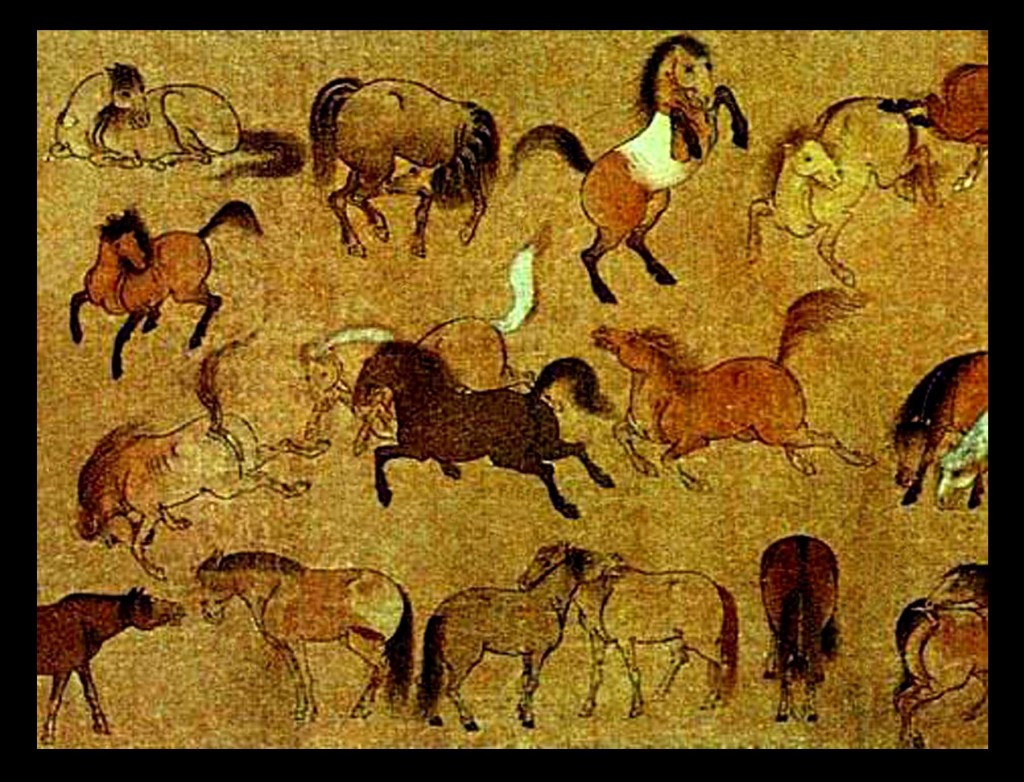
Artists from the Han (202 BC) to the Tang (618–906) dynasties mainly painted the human figure. Much of what is known of early Chinese figure painting comes from burial sites, where paintings were preserved on silk banners, lacquered objects, and tomb walls. Many early tomb paintings were meant to protect the dead or help their souls get to paradise. Others illustrated the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius, or showed scenes of daily life.
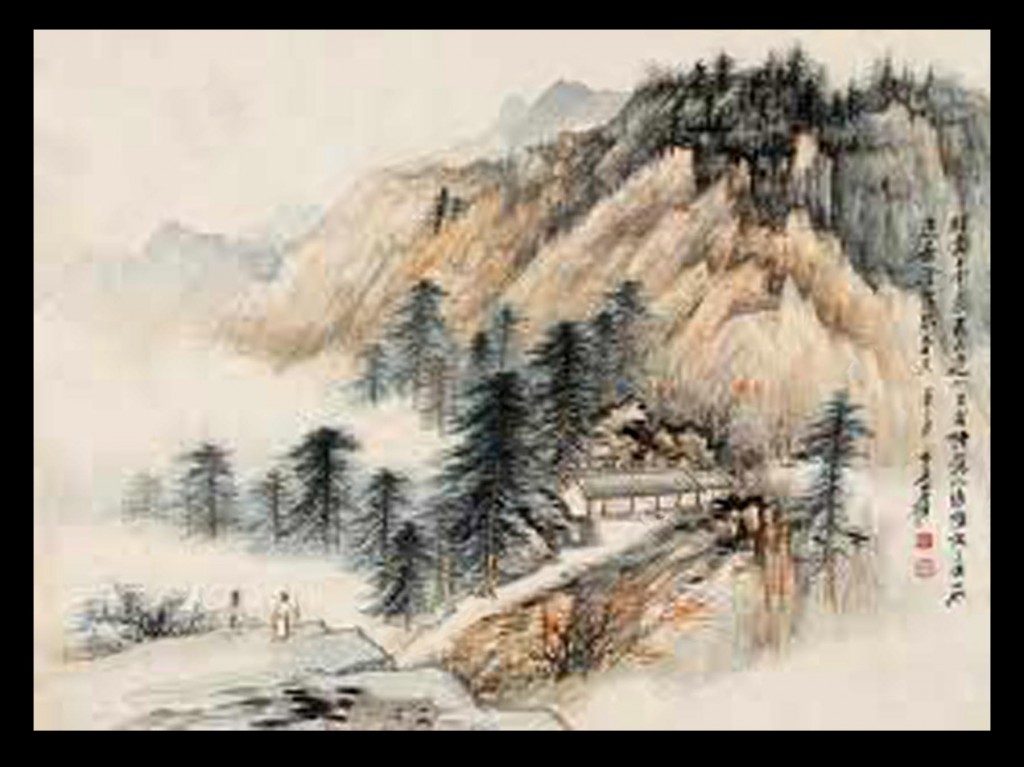
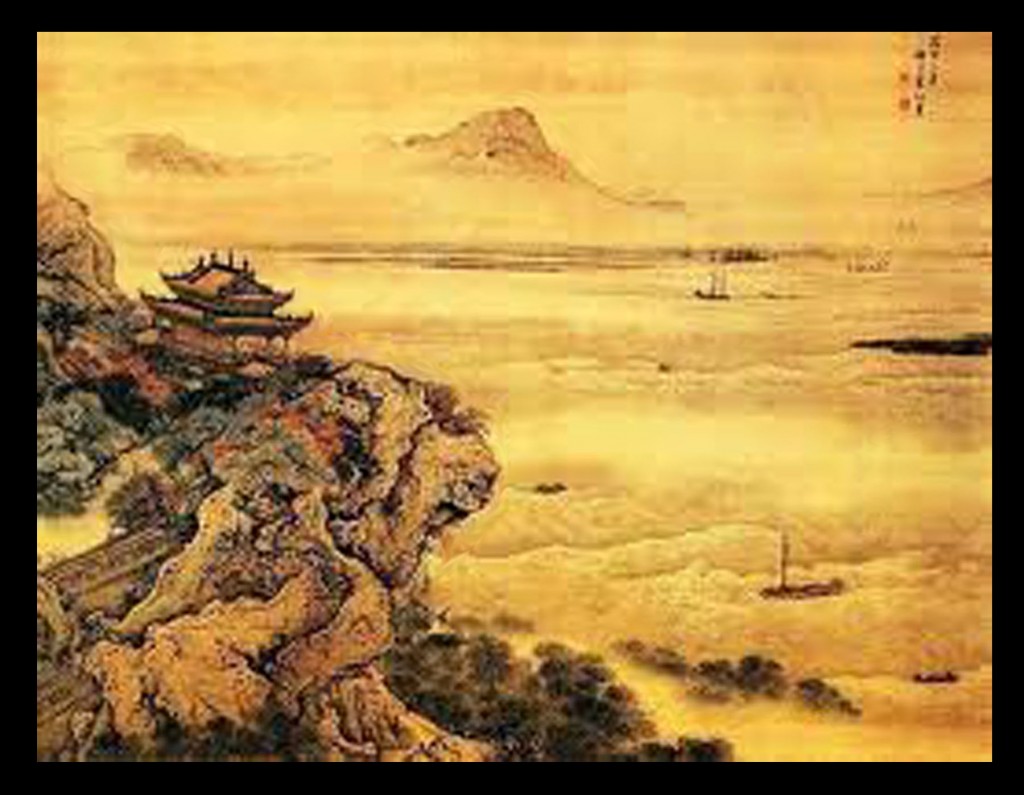
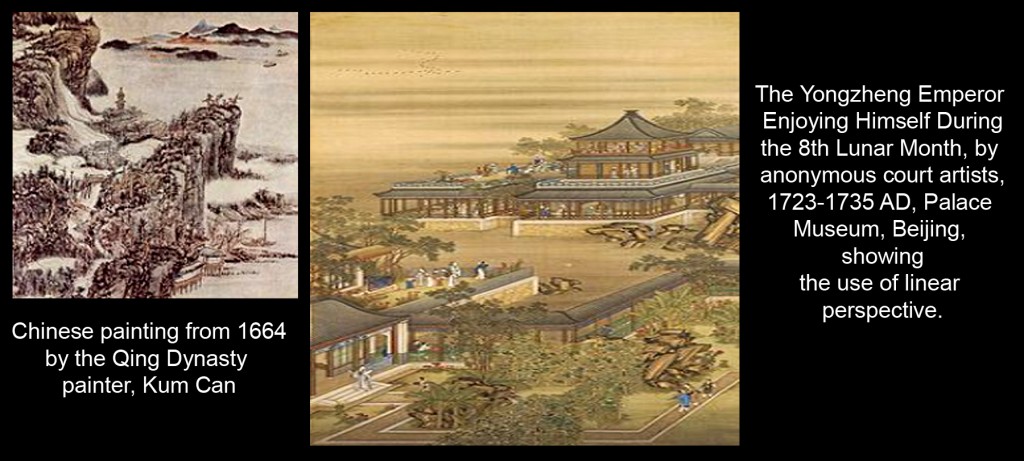
Many critics consider landscape to be the highest form of Chinese painting. The time from the Five Dynasties period to the Northern Song period (907–1128) is known as the “Great age of Chinese landscape”. In the north, artists such as Jing Hao, Li Cheng, Fan Kuan, and Guo Xi painted pictures of towering mountains, using strong black lines, ink wash, and sharp, dotted brushstrokes to suggest rough stone. In the south, Dong Yuan, Juran, and other artists painted the rolling hills and rivers of their native countryside in peaceful scenes done with softer, rubbed brushwork. These two kinds of scenes and techniques became the classical styles of Chinese landscape painting.
Sculpture
Chinese ritual bronzes from the Shang and Western Zhou Dynasties come from a period of over a thousand years from c. 1500, and have exerted a continuing influence over Chinese art. They are cast with complex patterned and zoomorphic decoration, but avoid the human figure, unlike the huge figures only recently discovered at Sanxingdui.[4] The spectacular Terracotta Army was assembled for the tomb of Qin Shi Huang, the first emperor of a unified China from 221–210 BCE, as a grand imperial version of the figures long placed in tombs to enable the deceased to enjoy the same lifestyle in the afterlife as when alive, replacing actual sacrifices of very early periods. Smaller figures in pottery or wood were placed in tombs for many centuries afterwards, reaching a peak of quality in the Tang Dynasty.[5]
Native Chinese religions do not usually use cult images of deities, or even represent them, and large religious sculpture is nearly all Buddhist, dating mostly from the 4th to the 14th century, and initially using Greco-Buddhist models arriving via the Silk Road. Buddhism is also the context of all large portrait sculpture; in total contrast to some other areas in medieval China even painted images of the emperor were regarded as private. Imperial tombs have spectacular avenues of approach lined with real and mythological animals on a scale matching Egypt, and smaller versions decorate temples and palaces.[6] Small Buddhist figures and groups were produced to a very high quality in a range of media,[7] as was relief decoration of all sorts of objects, especially in metalwork and jade.[8] Sculptors of all sorts were regarded as artisans and very few names are recorded.[9]
Pottery
Chinese ceramic ware shows a continuous development since the pre-dynastic periods, and is one of the most significant forms of Chinese art. China is richly endowed with the raw materials needed for making ceramics. The first types of ceramics were made during the Palaeolithic era, and in later periods range from construction materials such as bricks and tiles, to hand-built pottery vessels fired in bonfires or kilns, to the sophisticated Chinese porcelain wares made for the imperial court. Most later Chinese ceramics, even of the finest quality, were made on an industrial scale, thus very few individual potters or painters are known. Many of the most renowned workshops were owned by or reserved for the Emperor, and large quantities of ceramics were exported as diplomatic gifts or for trade from an early date.
Decorative arts
As well as porcelain, a wide range of materials that were more valuable were worked and decorated with great skill for a range of uses or just for display.[10] Chinese jade was attributed with magical powers, and was used in the Stone and Bronze Ages for large and impractical versions of everyday weapons and tools, as well as the bi disks and cong vessels.[11] Later a range of objects and small sculptures were carved in jade, a difficult and time-consuming technique. Bronze, gold and silver, rhinoceros horn, Chinese silk, ivory, lacquer, cloisonne enamel and many other materials had specialist artists working in them.
Early forms of art in Chinaare found in the Neolithic Yangshao culture (Chinese: ????; pinyin: Y?ngsháo Wénhuà), which dates back to the 6th millennium BCE. Archeological findings such as those at the Banpo have revealed that the Yangshao made pottery; early ceramics were unpainted and most often cord-marked. The first decorations were fish and human faces, but these eventually evolved into symmetrical–geometric abstract designs, some painted.
The most distinctive feature of Yangshao culture was the extensive use of painted pottery, especially human facial, animal, and geometric designs. Unlike the later Longshan culture, the Yangshao culture did not use pottery wheels in pottery making. Excavations have found that children were buried in painted pottery jars.
The Liangzhu culture was the last Neolithic Jade culture in the Yangtze River delta and was spaced over a period of about 1,300 years. The Jade from this culture is characterized by finely worked, large ritual jades such as Cong cylinders, Bi discs, Yue axes and also pendants and decorations in the form of chiseled open-work plaques, plates and representations of small birds, turtles and fish. The Liangzhu Jade has a white, milky bone-like aspect due to its Tremolite rock origin and influence of water-based fluids at the burial sites. Jade is a green stone that cannot be carved so it has to be ground.
The Bronze Age in China began with the Xia Dynasty. Examples from this period have been recovered from ruins of the Erlitou culture, in Shanxi, and include complex but unadorned utilitarian objects. In the following Shang Dynasty more elaborate objects, including many ritual vessels, were crafted. The Shang are remembered for their bronze casting, noted for its clarity of detail. Shang bronzesmiths usually worked in foundries outside the cities to make ritual vessels, and sometimes weapons and chariot fittings as well. The bronze vessels were receptacles for storing or serving various solids and liquids used in the performance of sacred ceremonies. Some forms such as the ku and jue can be very graceful, but the most powerful pieces are the ding, sometimes described as having the an “air of ferocious majesty.”
It is typical of the developed Shang style that all available space is decorated, most often with stylized forms of real and imaginary animals. The most common motif is the taotie, which shows a mythological being presented frontally as though squashed onto a horizontal plane to form a symmetrical design. The early significance of taotie is not clear, but myths about it existed around the late Zhou Dynasty. It was considered to be variously a covetous man banished to guard a corner of heaven against evil monsters; or a monster equipped with only a head which tries to devour men but hurts only itself.
The function and appearance of bronzes changed gradually from the Shang to the Zhou. They shifted from been used in religious rites to more practical purposes. By the Warring States Period, bronze vessels had become objects of aesthetic enjoyment. Some were decorated with social scenes, such as from a banquet or hunt; whilst others displayed abstract patterns inlaid with gold, silver, or precious and semiprecious stones.
Shang bronzes became appreciated as works of art from the Song Dynasty, when they were collected and prized not only for their shape and design but also for the various green, blue green, and even reddish patinas created by chemical action as they lay buried in the ground. The study of early Chinese bronze casting is a specialized field of art history.
Chuand Southern culture
A rich source of art in early Chinawas the state of Chu, which developed in the Yangtze River valley. Excavations of Chu tombs have found painted wooden sculptures, jade disks, glass beads, musical instruments, and an assortment of lacquerware. Many of the lacquer objects are finely painted, red on black or black on red. A site in Changsha,Hunan province, has revealed some of the oldest paintings on silk discovered to date.
The Terracotta Army, inside the Mausoleum of the First Qin Emperor, consists of more than 7,000 life-size tomb terra-cotta figures of warriors and horses buried with the self-proclaimed first Emperor of Qin (Qin Shi Huang) in 210–209 BC. The figures were painted before being placed into the vault. The original colors were visible when the pieces were first unearthed. However, exposure to air caused the pigments to fade, so today the unearthed figures appear terracotta in color. The figures are in several poses including standing infantry and kneeling archers, as well as charioteers with horses. Each figure’s head appears to be unique, showing a variety of facial features and expressions as well as hair styles.
Link to Ing’s Peace Proem Translated into Burma (Myanmar):
https://ingpeaceproject.com/ing-peace-project/ings-peace-poem-translated-into-burmese/